Stevia, a natural sweetener derived from the stevia rebaudiana plant, has rapidly gained popularity as a healthier alternative to sugar and artificial sweeteners. Known for its powerful sweetness and lack of calories, stevia has become a staple in health-conscious diets, especially for those looking to reduce sugar intake or manage conditions like diabetes and obesity.
We'll explore everything you need to know about stevia, including its history, benefits, potential side effects, and how it compares to other sweeteners.

Stevia, is a natural, plant-based sweetener that comes from the leaves of the stevia plant, native to south america. For centuries, indigenous people in paraguay and brazil used stevia leaves to sweeten teas and traditional medicines. The plant's sweet components, known as steviol glycosides, are extracted from the leaves and purified to create the sweetener used in modern food products.
Stevia is known for being 200 to 400 times sweeter than sugar, yet it contains zero calories. This powerful sweetness allows only small amounts of stevia to be used in recipes, making it a popular choice for those trying to reduce calorie intake without sacrificing taste.


How is stevia made?
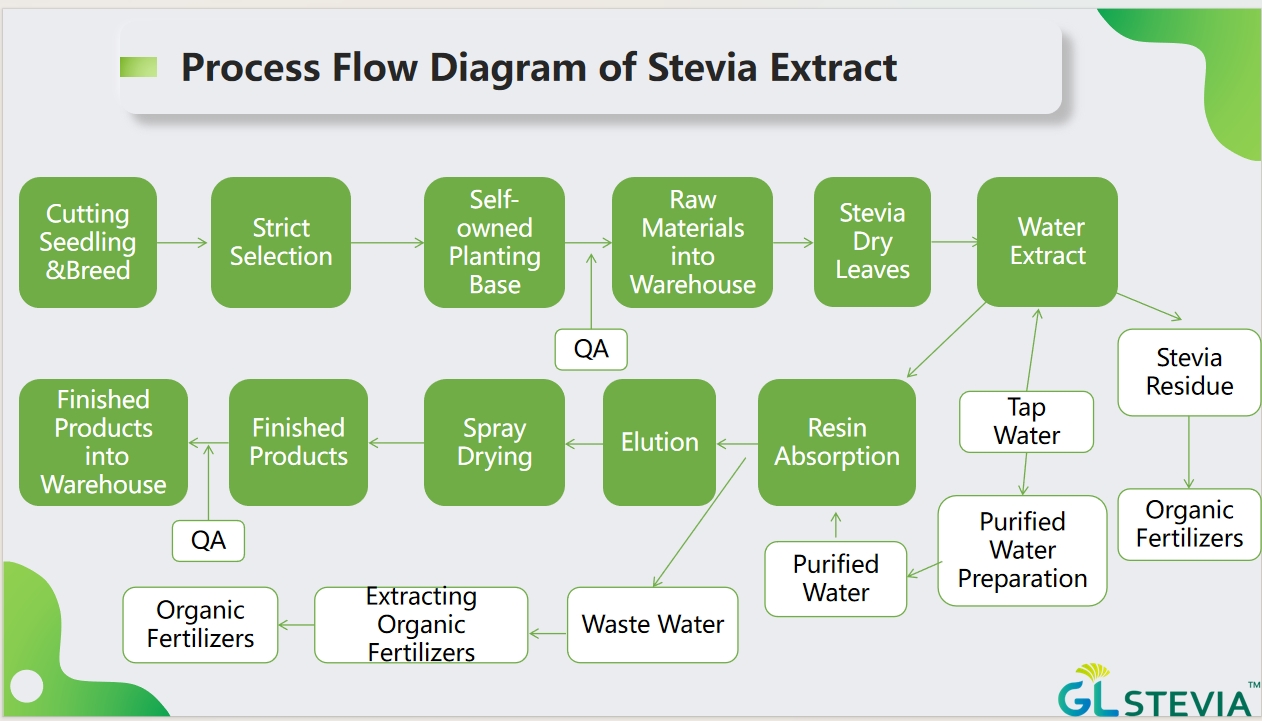
Stevia goes through a multi-step process to become the sweetener used in foods and beverages. Here's how it works:
Harvesting the stevia leaves: The stevia plant leaves are harvested and dried after reaching maturity.
Extraction: The dried leaves are soaked in water, allowing the sweet steviol glycosides (such as rebaudioside a, the most common sweet compound) to be extracted.
Purification: The extracted solution is then filtered and purified to remove impurities and ensure a concentrated form of steviol glycosides.
Drying and processing: The purified extract is dried and further processed into powders or liquid forms to be used as a sweetener in various food products.
Though the extraction process involves some refining, stevia remains a natural product in contrast to artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose.
Health benefits of stevia
Stevia is widely regarded for its numerous health benefits, especially as an alternative to sugar. Here are some of the most significant advantages of including stevia in your diet:
1. Zero calories
Stevia is a calorie-free sweetener, making it an excellent option for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight. Because stevia is so much sweeter than sugar, only a small amount is required to provide the same sweetness, reducing overall calorie intake in food and beverages.
2. Blood sugar control
One of the most important benefits of stevia is that it does not affect blood glucose levels. This makes it a perfect sugar substitute for people with diabetes or anyone trying to manage their blood sugar levels. Unlike sugar, which causes blood sugar spikes, stevia has a zero glycemic index, meaning it doesn't cause a rise in blood sugar after consumption.
Some studies have even suggested that stevia may have beneficial effects on insulin sensitivity, helping the body better manage glucose levels, though more research is needed to confirm this.
Potential side effects and concerns
While stevia is generally considered safe and has been approved by major health organizations like the fda and european food safety authority (efsa), some people may experience mild side effects or concerns.
Processing concerns
Although stevia is a natural product, many commercially available stevia sweeteners undergo extensive processing. Some brands may blend stevia with other sweeteners, including artificial ones, which can dilute its health benefits. It's important to read labels carefully and choose pure stevia products for a more natural option.
Stevia vs. Other sweeteners
1. Stevia vs. Sugar
Compared to sugar, stevia is a calorie-free, zero-carb option that does not cause blood sugar spikes. This makes it far superior for people managing diabetes or looking to control their calorie intake. Additionally, stevia doesn't contribute to tooth decay, unlike sugar, which can cause cavities.
However, in terms of taste, sugar may still be preferred by some consumers because stevia can have a slight bitter or licorice-like aftertaste, depending on the formulation.
2. Stevia vs. Artificial sweeteners (aspartame, sucralose)
Many consumers prefer stevia over artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose because of its natural origin. Artificial sweeteners are synthetic, and some studies have raised concerns about their long-term health effects, though they are still widely regarded as safe.
Stevia, being plant-derived, appeals to those seeking cleaner, more natural ingredients in their diets. In terms of safety, stevia also has fewer controversies compared to artificial alternatives, which have faced public scrutiny for potential links to health issues like cancer or neurological disorders.
3. Stevia vs. Honey
While honey is also considered a natural sweetener, it still contains calories and can raise blood sugar levels, making it less suitable for people with diabetes or those focused on weight management. Stevia is a better option for people looking for sweetness without the calories or sugar spikes associated with honey.
How to use stevia in your diet?
Stevia can be used in various forms, including powder, liquid, and even in raw leaf form. It is commonly found in:
· Beverages: Stevia is often used in coffee, tea, smoothies, and even flavored waters to replace sugar.
· Baking: Stevia can be used as a substitute for sugar in baked goods like cookies, cakes, and muffins, though adjustments to recipes may be needed due to stevia's high sweetness concentration.
· Condiments: Some sauces, salad dressings, and condiments use stevia as a sugar alternative.
· Yogurts and dairy products: Many low-calorie yogurts and dairy products incorporate stevia to reduce sugar content without sacrificing taste.


Stevia has emerged as one of the most popular sugar alternatives, particularly among health-conscious consumers. Its zero-calorie, natural origin, and ability to regulate blood sugar make it an excellent choice for those looking to reduce their sugar intake without sacrificing sweetness. While stevia may have a slightly different taste and some mild side effects, it remains a superior option compared to both sugar and artificial sweeteners.
Whether you're managing a health condition like diabetes or simply looking to make better dietary choices, stevia offers a natural and safe way to enjoy sweetness without the negative consequences of sugar.
Related Recommendation
All images in this article are sourced from: GL Stevia, Pexels, Natvia