As consumers become more health-conscious, the demand for natural sweeteners has surged, with stevia emerging as a popular alternative to sugars. As a natural high intensive sweetener, stevia is derived from the leaves of the stevia rebaudiana plant. However, many potential users are curious about one key question: stevia taste. This article delves into the flavor profile of stevia, its comparisons with other sweeteners, and its implications for culinary use.
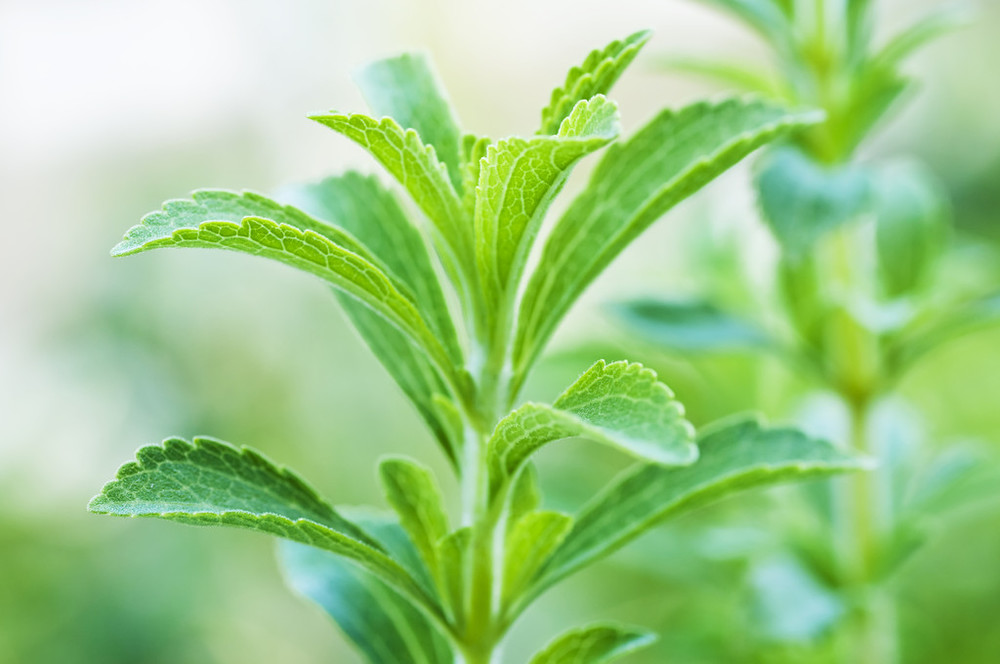

Stevia is a natural sweetener extracted from the leaves of the stevia rebaudiana plant, native to South America. The sweetness of stevia primarily comes from its glycosides, particularly stevioside and rebaudioside A, which can be up to 300 times sweeter than sugar. Because of this potency, only small amounts are needed to achieve the desired sweetness
The appeal of stevia
Consumers are drawn to stevia for several reasons:
· Calorie-Free: Unlike sugar, stevia has no calories, making it an attractive option for those looking to reduce caloric intake.
· Natural Origin: Many prefer stevia over artificial sweeteners due to its plant-based origin.
· Blood Sugar Friendly: Stevia does not raise blood glucose levels, making it suitable for people with diabetes.
2. The taste of stevia: sweetness and beyond
While the sweetness of stevia is appealing, its taste is not without complexities. Understanding its flavor profile is essential for anyone considering incorporating it into their diet.
Sweetness level
Stevia is incredibly sweet, with a sweetness potency that can reach up to 300 times that of table sugar. This means that a little goes a long way. Many consumers find that they can achieve the desired sweetness with a fraction of the amount they would typically use with sugar.
Flavor nuances
The taste of stevia is often described as having a clean, sweet profile, but it is essential to note that there can be some variations:
· Aftertaste: One of the most commonly reported characteristics of stevia is its aftertaste. Some users detect a slight bitterness or a licorice-like flavor lingering after the initial sweetness. This aftertaste can vary depending on the specific stevia product, as different formulations may have varying levels of glycosides.
· Bitterness: For some people, especially in high concentrations, stevia can impart a bitter taste, particularly if not blended well with other ingredients.
Quality variations
The taste of stevia can also differ significantly depending on the quality and form used:
· Refined Stevia Extracts: High-quality stevia extracts, particularly those that isolate rebaudioside A, tend to have a milder flavor profile with less bitterness. These extracts are commonly used in commercial products.
· Raw Stevia Leaf: The whole leaf or less refined forms of stevia may have a more pronounced flavor, including additional herbal notes and potential bitterness.
3. Stevia vs. other sweeteners
To better understand stevia's taste, it's helpful to compare it with other common sweeteners.
(1) SUGAR
· Taste: Sugar has a pure sweetness that is universally recognized and loved.
· Aftertaste: Sugar typically does not have an aftertaste, making it the baseline for sweetness comparison.
· Calories: Sugar contains calories, while stevia is calorie-free.
(2) ARTIFICIAL SWEETENERS (e.g., Aspartame, Sucralose)
· Taste: Some artificial sweeteners can have a chemical aftertaste that differs from the natural flavor of stevia.
· Health Perception: Many consumers prefer stevia due to its natural origins, while some view artificial sweeteners with skepticism.
(3) OTHER NATURAL SWEETENERS (e.g., Monk Fruit, Honey)
· Monk Fruit: Similar to stevia, monk fruit is a natural sweetener, often praised for its pleasant taste and minimal aftertaste.
· Honey: While honey adds a distinct flavor, it also contains calories, which makes it less appealing for those looking to reduce caloric intake.
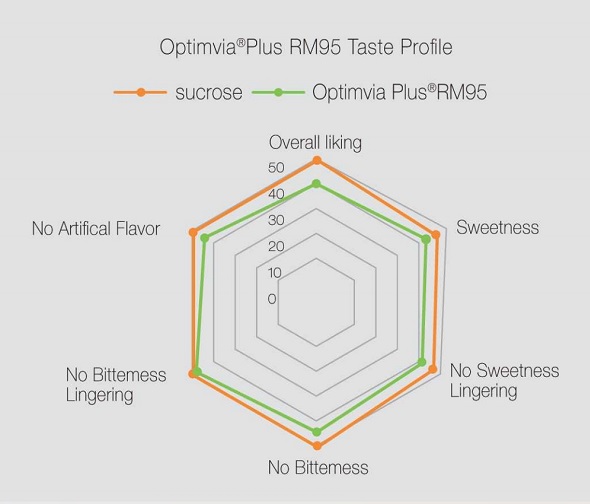

4. Culinary applications of stevia
Understanding stevia's taste is crucial when considering its use in cooking and baking. Here are some tips on how to incorporate stevia effectively:
Beyond natural sweeteners and reformulation techniques, there are other exciting trends that point to the future of sugar reduction:
(1) BAKING
When substituting stevia for sugar in baking, it's essential to account for its sweetness potency:
· Conversion: Use approximately 1 teaspoon of stevia for every cup of sugar, but check product instructions, as formulations may vary.
· Moisture and Bulk: Since stevia lacks bulk, consider adding additional moisture or using a bulking agent to achieve the right texture.
(2)BEVERAGE
Stevia is often used in beverages, from smoothies to teas:
· Mix Well: Ensure that stevia is thoroughly mixed into the liquid to minimize any aftertaste.
· Pairing: Combining stevia with flavors like citrus, vanilla, or spices can enhance its sweetness and mask any bitterness.
(3) SAUCES AND DRESSINGS
Stevia can be a great addition to sauces and dressings:
· Balancing Flavors: Use stevia to balance the acidity in vinaigrettes or sauces without adding calories.
· Experiment: Adjust the amount based on personal taste; a little can go a long way.
5. Consumer perceptions and trends
Despite the numerous benefits of stevia, consumer perceptions of its taste can influence its market acceptance. Surveys have shown mixed reviews, with some consumers embracing stevia for its natural qualities, while others remain wary due to taste concerns.
POSITIVE TRENDS
· Increased Awareness: As health trends continue to rise, more consumers are willing to experiment with stevia, particularly as education around its benefits spreads.
· Product Innovation: Companies are creating blends of stevia with other sweeteners to improve taste, further promoting its use.
CHALLENGES
· Taste Acceptance: Overcoming the initial taste barriers remains a challenge for stevia to gain widespread acceptance, especially among those accustomed to traditional sugar.


Embracing stevia's unique taste
Stevia offers a compelling alternative to sugar, with its natural sweetness and zero calories making it an attractive choice for health-conscious consumers. While its taste can present challenges, particularly with aftertaste, innovations in product formulation and consumer education are helping to mitigate these concerns.
By understanding the complexities of stevia's flavor profile and effectively incorporating it into culinary practices, consumers can enjoy the benefits of this natural sweetener without sacrificing taste. As the demand for healthier alternatives continues to grow, stevia is well-positioned to play a significant role in the future of sweetening options.
Related Recommendation
All images in this article are sourced from: GL Stevia, Freepik,